
Literature Review vs. Annotated Bibliography
For those of you who are engaged in a research project or composing a thesis in the United States, whether at the undergraduate, postgraduate, or PhD level, it might be curious to discover the difference between annotated bibliography and literature review.
Both components play crucial roles in a research paper, providing context for the cited sources related to a specific academic problem. While a literary review emphasizes the significance of a paper's findings, an annotated reference list centers on assessing the quality, validity, and relevance of the information.
What Is a Literature Review?
A literature review is a critical and comprehensive survey of existing scholarly works relevant to a particular topic or question. It involves systematically examining, summarizing, and synthesizing published studies, articles, books, and other sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge on the chosen subject. The primary goal of a literary analysis is to identify gaps, patterns, and trends in the existing written matter, enabling researchers to position their work within the broader context of the field. It not only showcases the depth of one's understanding of the subject but also helps justify the need for new investigation by highlighting areas where further investigation or clarification is warranted. If you're wondering, "Who can write my literature review for me?" this process can indeed be meticulous but ultimately rewarding.

What Is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is a compilation of citations for various sources such as books, articles, and other materials relevant to a specific topic. What sets it apart from a traditional list of references is the inclusion of concise annotations after each citation. These annotations serve as brief summaries and evaluations of the material, offering insights into the main ideas, key arguments, and methodologies presented. The purpose of a commented bibliography is to provide scholars with a quick overview and critical assessment of the available literary works on a particular subject.
By summarizing and evaluating each book, it aids students in determining the quality, validity, and relevance of the materials they consult. The annotations also play a crucial role in helping learners situate each piece of evidence within the broader context of their study. As a valuable organizational tool, an annotated bibliography assists in managing and synthesizing information, guiding the academician in selecting the most pertinent materials for further exploration and contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of the research landscape. If you’re in a hurry, you can write us, so any of our annotated bibliography writer can lend you a helping hand today.
Annotated Bibliography
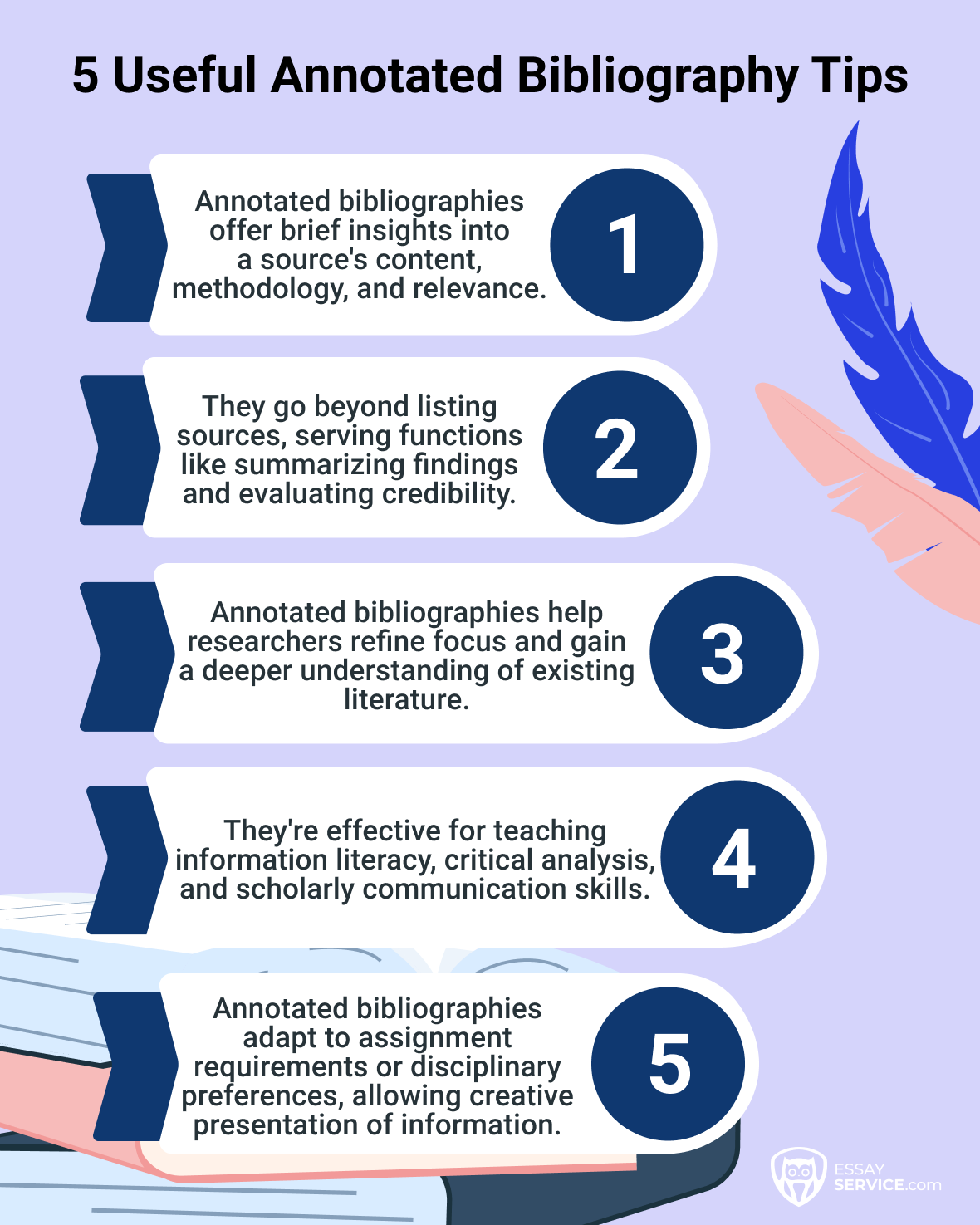
Purpose
An annotated bibliography serves multiple purposes in academic exploration. Its primary goal is to provide a comprehensive overview of the existing writing material on a specific topic. Annotations offer brief summaries and critical evaluations of each book, aiding students in assessing the quality, relevance, and methodology of the materials. Additionally, an annotated reference list helps learners organize their sources, identify key themes, and justify the inclusion of each citation in the context of their study. It is a valuable tool for scholars seeking to understand the existing knowledge landscape and identify gaps for further exploration.
Structure
The structure of an annotated bibliography typically includes a citation for each source followed by a concise annotation. Citations adhere to a specific citation style, such as Chicago, APA, or MLA. The entire reference list often follows a consistent formatting style, such as hanging indents. Annotations are usually written in paragraph form, with a clear and concise summary of the main ideas and a critical evaluation of its strengths and weaknesses.
Components
Citation
- Each entry begins with a properly formatted citation providing details like author(s), title, publication information, and relevant dates.
Summary
- The annotation includes a brief summary of the main ideas, arguments, and methodology, highlighting key elements that are relevant to the topic question.
Evaluation
- A critical evaluation follows the summary, assessing the material's credibility, validity, and overall contribution to the field. It may discuss the author's perspective, methodology, and potential limitations.
Literature Review
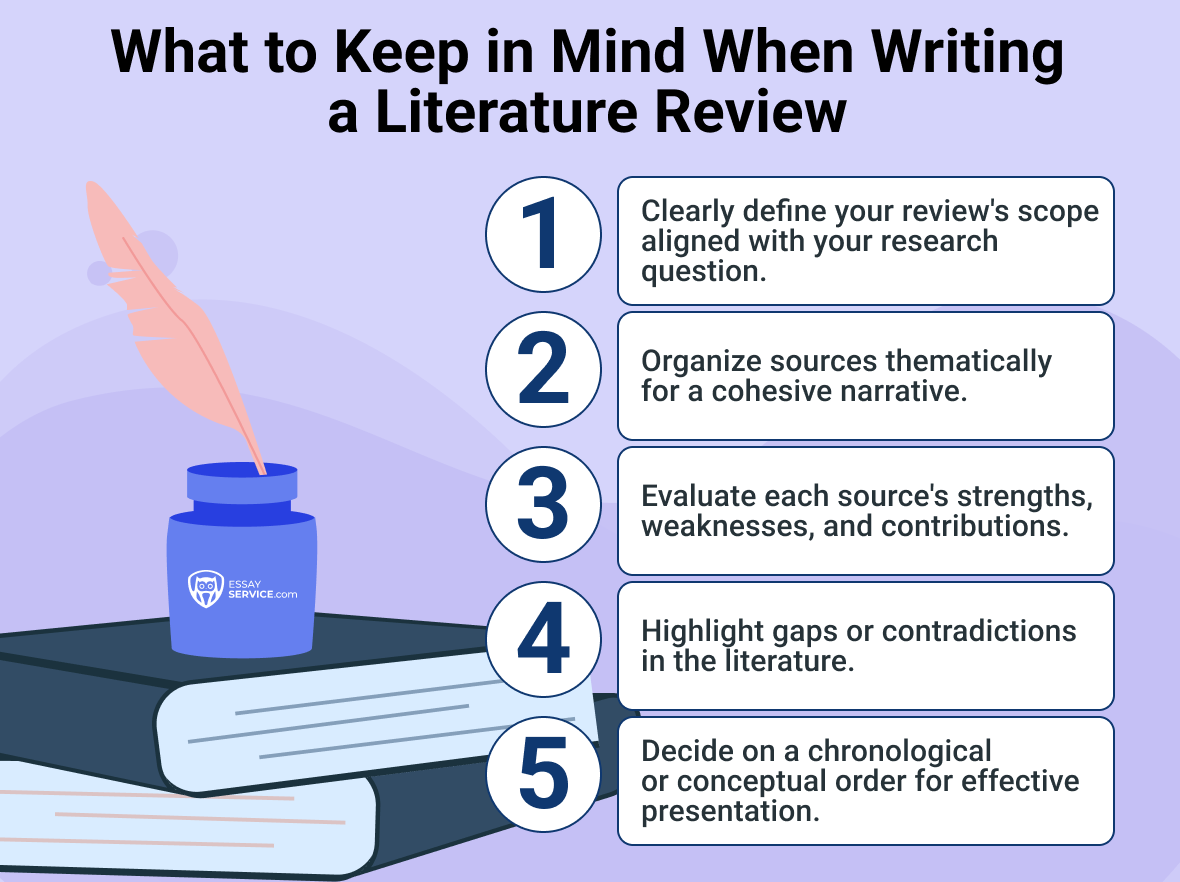
Purpose
A literature review serves the purpose of critically examining and summarizing existing scholarly contributions on a specific topic or question. It aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the current state of knowledge in a particular field, identify gaps, trends, and patterns, and establish the context for a new investigation. The primary goal is to showcase the writer's familiarity with relevant studies, theories, and methodologies while justifying the need for their own investigation.
Structure
The structure of an evaluation typically follows a coherent and organized format. It begins with an introduction that defines the scope and purpose of the overview. The content is organized thematically, chronologically, or methodologically, presenting a synthesis of the key findings from various texts. It concludes with a summary that emphasizes the significance of the reviewed literary texts and highlights areas for further analysis.
Components
Introduction
- Clearly defines the scope and purpose of the assessment, outlining the essential question or problem addressed.
Body
- Organized by themes, methodologies, or chronology, this section synthesizes key concepts, findings, and debates from various origins.
Analysis and Discussion
- Critically evaluates and discusses the strengths, weaknesses, and contributions. It may identify common themes, controversies, or gaps in the literature.
Conclusion
- Summarizes the main findings of the literature review, highlights its significance in the context of the broader academic field, and suggests potential avenues for future surveys.
Key Differences to Keep in Mind
Annotated bibliographies and literature reviews are common components of academic writing, especially in scholarly papers, theses, and dissertations. However, they serve distinct purposes and have different formats. Here are the key differences every student should know:
- The primary purpose of a commented bibliography is to provide a list of citations to relevant books, articles, etc., along with a brief summary or evaluation. It helps the reader to understand the content, quality, and relevance of the topic.
- The main purpose of a literature review is to provide a comprehensive overview and synthesis of existing grounding on a specific topic. It involves analyzing, summarizing, and organizing the existing texts to highlight gaps, contradictions, and areas of consensus.
- Each citation is followed by a concise annotation (summary, evaluation, or reflection) that describes the content, methodology, and relevance to the paper’s topic.
- A literature assessment involves a narrative overview, presenting key concepts, theories, methodologies, and findings from various sources. It aims to provide a coherent and integrated overview of the current state of knowledge on the topic.
- In an annotated bibliography, each annotation is typically brief, usually a paragraph or a few sentences summarizing the main points.
- A literary review is a more extensive and in-depth inspection that may span several pages or even chapters, depending on the given scope.
- Annotated bibliography entries are typically arranged alphabetically or chronologically, and each entry stands alone.
- A literature review involves a thematic or chronological organization, grouping sources based on common themes, concepts, or topical questions.
- Each annotation includes a brief evaluation or reflection on the source, but the analysis tends to focus more on summarizing the content.
- A publication analysis requires a more critical analysis of the sources, examining the strengths and weaknesses of each study, identifying gaps in the existing knowledge, and discussing the overall contributions of the literature to the topic.
Frequently asked questions
New posts to your inbox!
Your submission has been received!



 (1) (1).webp)